| The Greenhouse Effect | |
|
There is now international consensus by a body called the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) that the Earth's temperature is increasing and that this increase is caused by human activity. To understand what is happening and relate it to our own environmental activities we need to look first at the greenhouse effect. |
|
|
The Earth's atmosphere acts in a similar way to a greenhouse in trapping energy from the Sun, and this is why the Greenhouse effect is so called. Imagine that the atmosphere behaves like the glass in a greenhouse. |
|
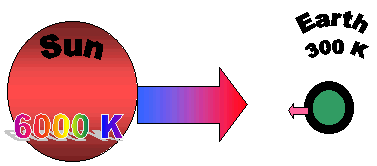
The Earth-Sun relationship with Earth's present atmosphere (shown as a black ring). The sun radiates a wide range of wavelengths. The Earth is much colder and so radiates principally in the IR. |
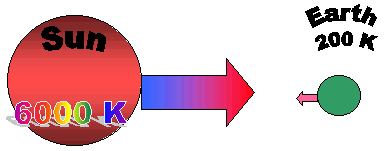
| The Earth-Sun relationship without an atmosphere. The Earth would lose more heat and so be much colder. |
|
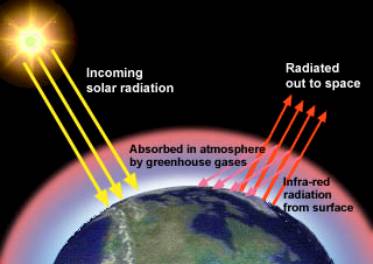
| The surface temperature of the sun is about 6000K and the sun radiates energy at short wavelengths, such as the visible and the UV parts of the spectrum as well as the longer wavelength infrared rays. |
|
|
UV rays are very harmful to humans, causing sunburn and skin cancers amongst other effects. Each photon or package of rays from the sun contains a lot of energy and it is mostly these rays which warm the ground, the surroundings and the air around us. The surface of the Earth is usually at a temperature of about 300K and would be much colder if the atmosphere did not cover it. In fact the atmosphere allows most of the sun's light to pass through and reach the surface of the Earth. In warming the land and air the suns rays are converted to thermal energy, but because these objects are only at 300K they radiate in the Infra Red part of the spectrum. This part is invisible to the naked eye and you might have seen night vision equipment or PIRs which are sensitive to these long wavelengths. |