| Cyclones (1) |
|
|
Cyclones are amongst the commonest of pollution prevention devices. They work by forcing the effluent flow to take a spiral path and thus make use of the so-called centrifugal force on the particles. Particles with sufficient inertia are thrown outwards and downwards as the gas flow deviates from a straight line. The heavier the particle the greater the tendency to be thrown out of the air stream. |
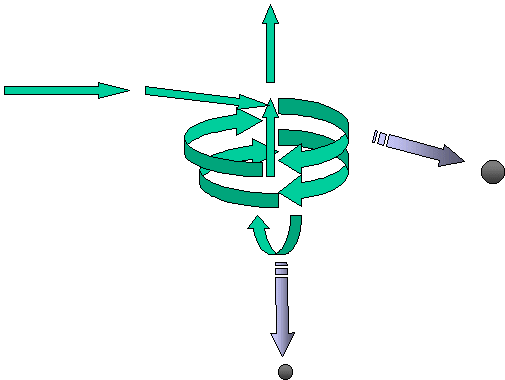 |
|
|
Larger particles are collected on the walls of the cyclone after being thrown outwards into an area close to the walls where the air velocity is essentially zero. |
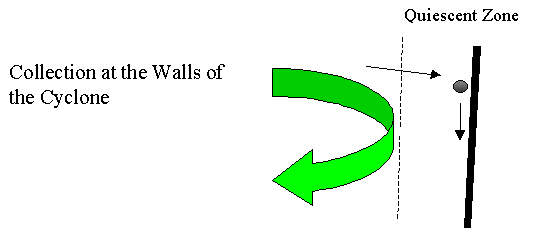 |