Cp is calculated without reference to the nominal, and it assumes that the outputs of the process are normally distributed (i.e. the distribution forms a symmetrical bell-shaped curve). The index is calculated using the formula:
Where the specification width is the measure of the customer's specified tolerance, and the process spread is 6 sigma units (1 sigma unit being an estimate of the process' standard deviation).
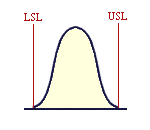
To get a better understanding of Cp values, it may be helpful to view it graphically. For a Cp of 1, the natural process spread is the same as the specification width, so the process spread will fit into the specified tolerance just once:
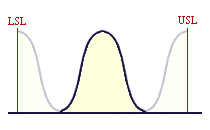
For a Cp of 2, the natural process spread is only half the specification width, and so the process spread will fit into the specified tolerance twice:
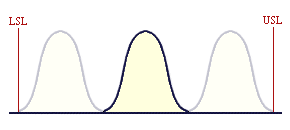
For a Cp of 3, the natural process spread is only one third of the specification width, and so the process spread will fit into the specified tolerance threee times: