| Sustainable Business Development |
|
Sustainable Business Performance |
|
Business has entered into a new phase in which sustainable business performance is regarded as:
Consumers demand that goods and services be produced by socially and environmentally responsible companies. Bankers and investors evaluate companies and make decisions, considering both environmental risks and environmental market opportunities. Consequently, more companies are discovering the benefits of going beyond regulatory compliance, toward sustainability. |
| Figure 10 |
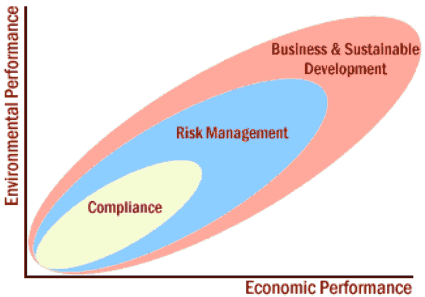 |
| (The Business and Sustainable Development (BSD) website) |
|
Initial Step Regulatory Compliance Compliance is fundamental to any business operation. Growth in national and international environmental laws and regulations is increasing the pressure on companies to improve environmental performance and avoid financial liabilities. If companies only operate within the vision of compliance then eventually they may fail to anticipate environmental liabilities, and in implementing "end of pipe" pollution or waste controls the opportunity for the company to establish efficient cost control systems and growth strategies is far reduced. Secondary development Step: Environmental Risk Management This can provide companies with an increased time element, i.e. implementing risk assessment and reviewing operational methods improves the company's ability to anticipate problems and prevent liability. In addition if carried out efficiently it can enable companies to consider more pro-active future strategies. Some companies conduct environmental health and safety (EHS) assessments, develop environmental policies and implement environmental management systems (EMS) in support of this. Environmental Risk Management can enable companies to reduce operational and insurance costs can be reduced through waste minimisation, pollution prevention and the reduction of health and safety hazards. |
| Figure 11 |
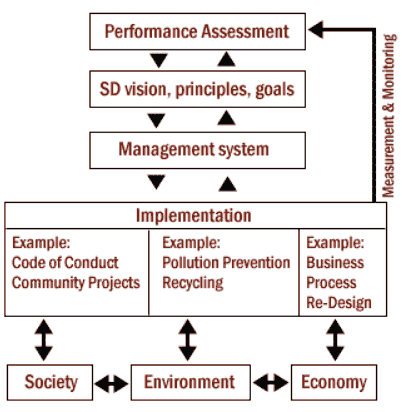 |
|
Final Step: Sustainable Development In the final step the business is driven with sustainability as the foundation. Sustainable concepts are integrated into all business strategies. Figure 11 illustrates the essential elements of an integrated sustainable management system. The company operates with an attitude of renewability and opportunity and seeks to achieve environmental quality, increase wealth and enhance competitive advantage. Management considers the long term interests and needs of the stakeholders. Results should include new business processes with reduced external impacts, improved financial performance and reputation among communities and stakeholders. The risks of new market development are falling as pressures for sustainable development grow. Some form of climate change policy will be instituted fairly soon. Developing a product now that reduces electrical needs, for example, may find a very small niche. But when the anticipated policy changes take place, the company will be well positioned in a dramatically expanding market. Regardless of the business case for prevention, generating revenue will always be the paramount goal. Few chief executives attain their position by cutting costs. The choices a company makes about where to invest its capital, what products to provide, and where to sell them are the most important determinants of long-term business success. The concepts of sustainable development sit well within such a framework. |